高性能紙コーティング材開発、マイクロプラスチック汚染削減へ 韓国
韓国科学技術院(KAIST)は5月22日、延世大学校(Yonsei University)との共同研究チームが生分解性に優れ、かつ高性能な紙コーティング材を開発したと発表した。この研究成果は、Green ChemistryとFood Chemistryに掲載された。
紙包装の低バリア性を改善するためのコーティング材としては一般に、ポリエチレン(PE)やエチレン・ビニルアルコール(EVOH)が使用されているが、分解されないため、自然環境に廃棄されるとマイクロプラスチック汚染の悪化につながる。バイオ由来物質や生分解性プラスチックを使用した包装材料も開発されているが、包装性能が向上するにつれ生分解性が低下するという課題があった。
KAISTの土木・環境工学科(Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering)のミョン・ジェウク(Myung Jaewook)教授らと延世大学校の包装物流学科(Department of Packaging and Logistics)のソ・ジョンチョル(Seo Jongcheol)教授率いる研究チームは、生分解性プラスチックであるホウ酸架橋ポリビニルアルコール(PVA)を用いて紙をコーティングし、生分解性、バリア性、強度を向上させた。開発されたコート紙は、従来のプラスチックに比べて優れた性能を示し、高湿度の条件下でも優れたバリア性と物理的強度を発揮した。
研究チームはまた、開発したコート紙の持続可能性を体系的に評価するため、生分解性と生体適合性についても詳細な検討を行った。生分解性条件が厳しいことで知られる海洋環境をシミュレートした評価では、59~82%の生分解を達成した。また、高い生体適合性も確認された。
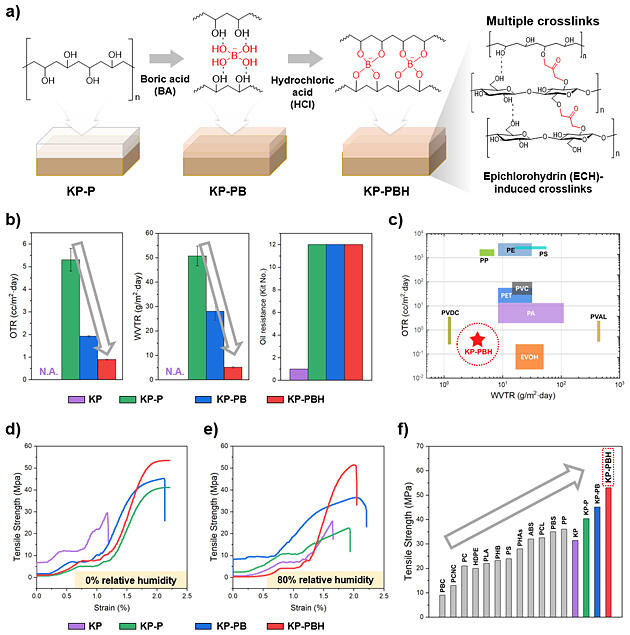
図1. (a) Chemical structure of boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coating on paper, (b-c) Oxygen and water vapor barrier properties, (d-f) Tensile strength in dry and moist conditions. OTR: Oxygen transmission rate, WVTR: Water vapor transmission rate.
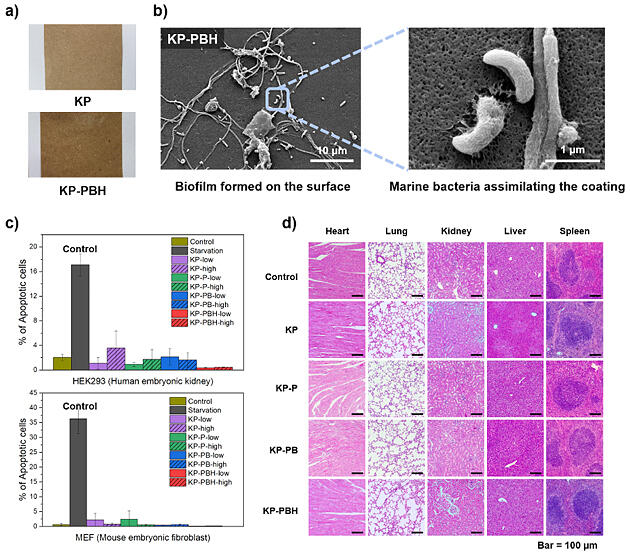
図2. (a) Normal paper and boric acid-crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol) coated paper, (b) Biodegradation of the coated paper by marine bacteria, (c) Result of cytotoxicity test using human embryonic kidney and mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. (d) Vital organs after one-month exposure of the coated papers to mice.
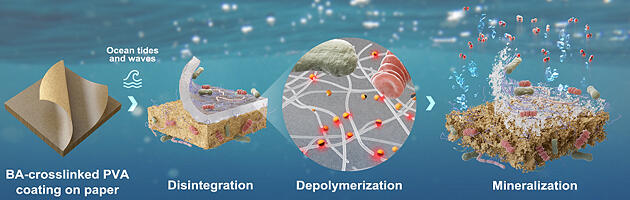
図3. End-of-life scenario of papers coated by BA-crosslinked PVA in the marine environment. The coated papers potentially be disintegrated by marine microorganisms and ocean waves and tides. The depolymerization of PVA coating and paper is then mediated by extracellular depolymerases such as oxidases and cellulases, after which the small subunits (oligomers and monomers) are assimilated by microbial cells. The carbon components in the coated papers are ultimately mineralized into CO2, posing no harm in the ocean.
(出典:いずれもKAIST)
サイエンスポータルアジアパシフィック編集部






